The Energy Intensity of the Internet: Edge and Core Networks
Status:: 🟩
Links:: Energy consumption of network communication
Metadata
Authors:: Hilty, Lorenz M.; Aebischer, Bernard
Authors:: Schien, Daniel; Coroama, Vlad C.; Hilty, Lorenz M.; Preist, Chris
Title:: The Energy Intensity of the Internet: Edge and Core Networks
Date:: 2015
Publisher:: Springer International Publishing
URL:: https://link.springer.com/10.1007/978-3-319-09228-7_9
DOI:: 10.1007/978-3-319-09228-7_9
Bibliography
Schien, D., Coroama, V. C., Hilty, L. M., & Preist, C. (2015). The Energy Intensity of the Internet: Edge and Core Networks. In L. M. Hilty & B. Aebischer (Eds.), ICT Innovations for Sustainability (Vol. 310, pp. 157–170). Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-09228-7_9
Zotero
Type:: #zotero/conferencePaper
Keywords:: []
Relations
Abstract
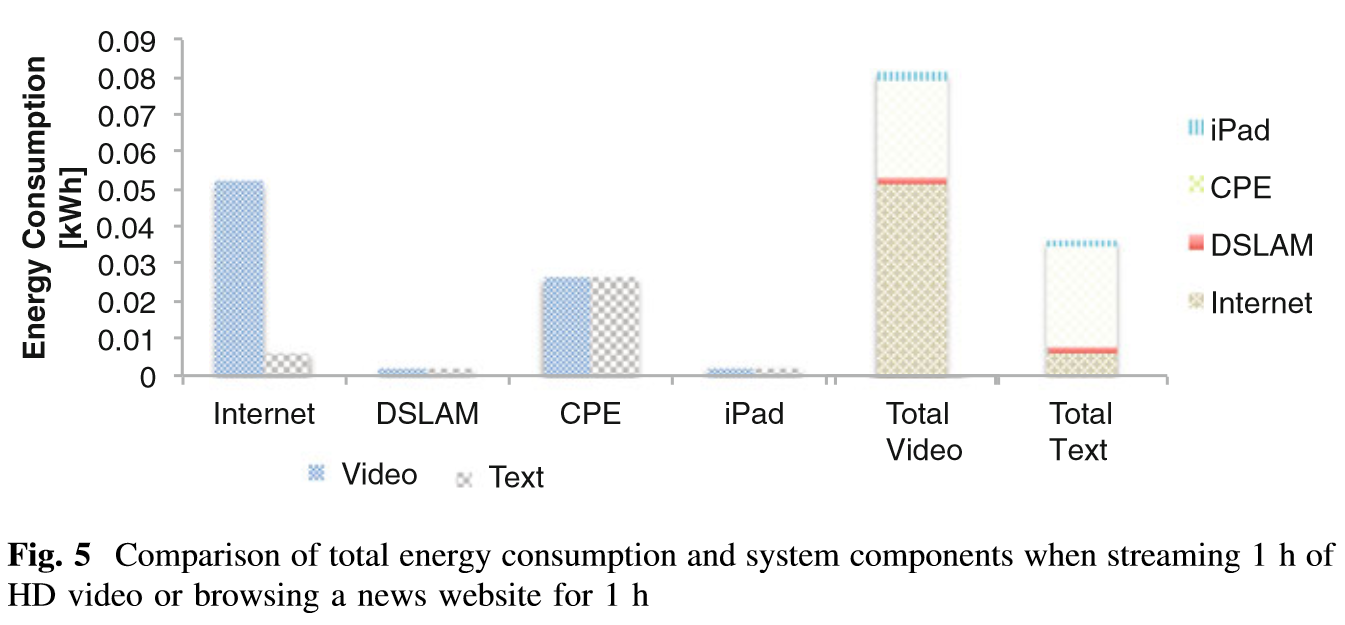
Environmental assessments of digital services seeking to take into account the Internet’s energy footprint typically require models of the energy intensity of the Internet. Existing models have arrived at conflicting results. This has lead to increased uncertainty and reduced comparability of assessment results. We present a bottom-up model for the energy intensity of the Internet that draws from the current state of knowledge in the field and is specifically directed towards assessments of digital services. We present the numeric results and explain the application of the model in practice. Complementing the previous chapter that presented a generic approach and results for access networks and customer premise equipment, we present a model to assess the energy intensity of the core networks, yielding the result of 0.052 kWh/GB.
Notes & Annotations
📑 Annotations (imported on 2023-06-23#14:07:24)
Given the above variable values and model structure, the average energy intensity of data traffic through edge, metro and long haul networks including an undersea cable link, but excluding access networks, evaluated to Kilowatt-hours per Gigabyte (kWh/GB) 0.052 kWh/GB.
Given the parameters provided for customer premise network equipment and the DSL access multiplexer, and allowing for overheads for idle standby of customer equipment, we estimate that the effective power consumption per subscriber household is about 52 W. Thus, the total energy consumption of a service can be described as:
E(S) = t(S) * 52 W + GB(S) * 0.052kWh/GB
where t(S) is the time of the service, 52 W the estimate for the average consumption of access networks and CPE, GB(S) the amount of data sent and received by the service (measured in GB), and 0.052 kWh/GB the estimate for the average energy intensity of long haul and metro networks.