Cloud Computing Sustainability
Compared to traditional data centers, 30_Knowledge/Cloud Computing has reduction potentials in terms of energy and resources, but also brings risks due to rebound effects, among other things.
Promises by Cloud Providers
- 2024-09-15: Data center emissions probably 662% higher than big tech claims. Can it keep up the ruse? | The Guardian →Omnivore
- 2024-07-17: Sustainability: How Did Amazon, Azure, Google Perform in 2023? - The New Stack by Adrian Cockcroft
- 2024-07-15: How Amazon Matches Power Needs to Green Energy Sources - The New Stack
- 2024-07-09: Microsoft and Google’s GHG emissions gains call viability of net-zero targets into question | Computer Weekly
- 2022-10-26: Are the CO2 emission reductions promised by cloud providers realistic? by Boavizta
Shared Responsibility Model
AWS and Azure use the "shared responsibility model" to communicate that there are different responsibilities for customers and the provider.
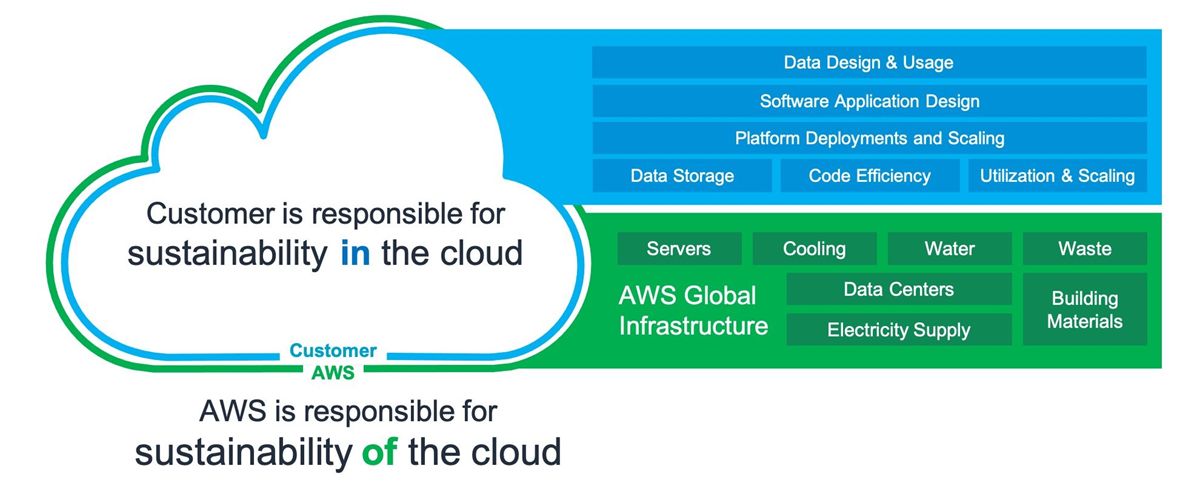
Source: The shared responsibility model (@AmazonWebServices.2023.SustainabilityPillarAWS)
Sustainability of the cloud: lower carbon footprint and more energy efficient than typical on-premises alternatives
Sustainability in the cloud: energy reduction and efficiency across all components of a workload
Sustainability through the cloud: workloads are designed to support wider sustainability challenges
Infrastructure Side
Overview:
- David Mytton: Energy and water consumption in IT - How to reach sustainability in computing - YouTube (from 2021)
Sustainability of Cloud Providers
Hyperscaler:
- Sustainability of the AWS Cloud
- Sustainability of the Google Cloud
- Sustainability of the Azure Cloud
See also Enabled Emissions by AI.
Other Providers:
Electricity Consumption & Carbon Emissions
Carbon Emissions of Cloud Computing
Energy Consumption & Carbon Emissions of Data Centers
How to make data centers low-carbon?
Environmental Risks
Negative Environmental Aspects of Cloud Computing
Software Side
Responsibility of Software
Energy-efficient Deployment and Operation of Software in the Cloud
Resiliency & Sustainability in the Cloud
CNCF Sustainability Landscape
For an overview see the Cloud Native Sustainability Landscape by the CNCF TAG Environmental Sustainability.
Reporting of Carbon Emissions
Cloud Carbon Dashboards & APIs
Standards
- Sustainable Data Centers > Metrics
- Workload Carbon Footprint Standard
- Technology Carbon Standard
- Software Carbon Intensity Specification by the Green Software Foundation